How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, insightful inspections, and exciting recreational pursuits. This guide provides a structured approach, taking you from pre-flight checks and fundamental controls to mastering advanced flight techniques and understanding legal regulations. Whether you’re a complete novice or looking to refine your skills, prepare to unlock the potential of unmanned aerial vehicles.
We’ll cover everything from the basic mechanics of controlling your drone – understanding throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll – to more advanced concepts like GPS stabilization and optimal camera settings for breathtaking aerial photography and videography. We’ll also delve into essential safety procedures, legal compliance, and routine maintenance to ensure the longevity and safe operation of your drone.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, verifying system functionality, and understanding potential risks. Failing to conduct a proper pre-flight check can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, or even injury.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone is in optimal condition for flight. This includes checking the battery level, inspecting the propellers for damage, and verifying a strong GPS signal. These steps are critical for preventing unexpected malfunctions during flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
This checklist provides a step-by-step guide for beginners to ensure a safe and successful flight. Remember to always consult your drone’s specific manual for detailed instructions.
| Item | Check | Notes | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Sufficient charge? | Check your drone’s battery indicator. Ensure the battery is fully charged or at least at the manufacturer’s recommended minimum level. | Charge battery if necessary. |
| Propellers | Securely attached and undamaged? | Inspect each propeller for cracks, bends, or other damage. Ensure they are firmly attached to the motors. | Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal | Strong signal? | Ensure the drone has a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS reception. The number of satellites should be sufficient (typically 8 or more). | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if necessary. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Properly calibrated and functioning? | Check for smooth movement and proper alignment. | Calibrate gimbal if necessary. Consult your drone’s manual for instructions. |
| Flight Controller | Firmware updated? | Ensure your drone’s firmware is up to date for optimal performance and safety features. | Update firmware if necessary. |
| Surroundings | Safe and legal flight area? | Check for obstacles, people, and restricted airspace. | Choose a different location if necessary. |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to react in emergencies is vital for safe drone operation. Understanding potential problems and their solutions can prevent accidents and minimize damage.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually control the drone back to the pilot’s location, prioritizing safety and avoiding populated areas.
- Battery Failure: Initiate RTH immediately if possible. If not, carefully guide the drone to a safe landing area, prioritizing a soft landing to minimize damage.
- Unexpected Malfunction: Attempt to land the drone safely in a clear area, away from people and obstacles. If a safe landing is not possible, initiate RTH if available. Analyze the cause of the malfunction after landing.
Safety Guidelines
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly your drone near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Always follow local and national regulations regarding drone operation.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Never fly your drone under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Keep your drone’s battery charged and in good condition.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section will cover basic controls, flight modes, and control interfaces.
Basic Drone Controls
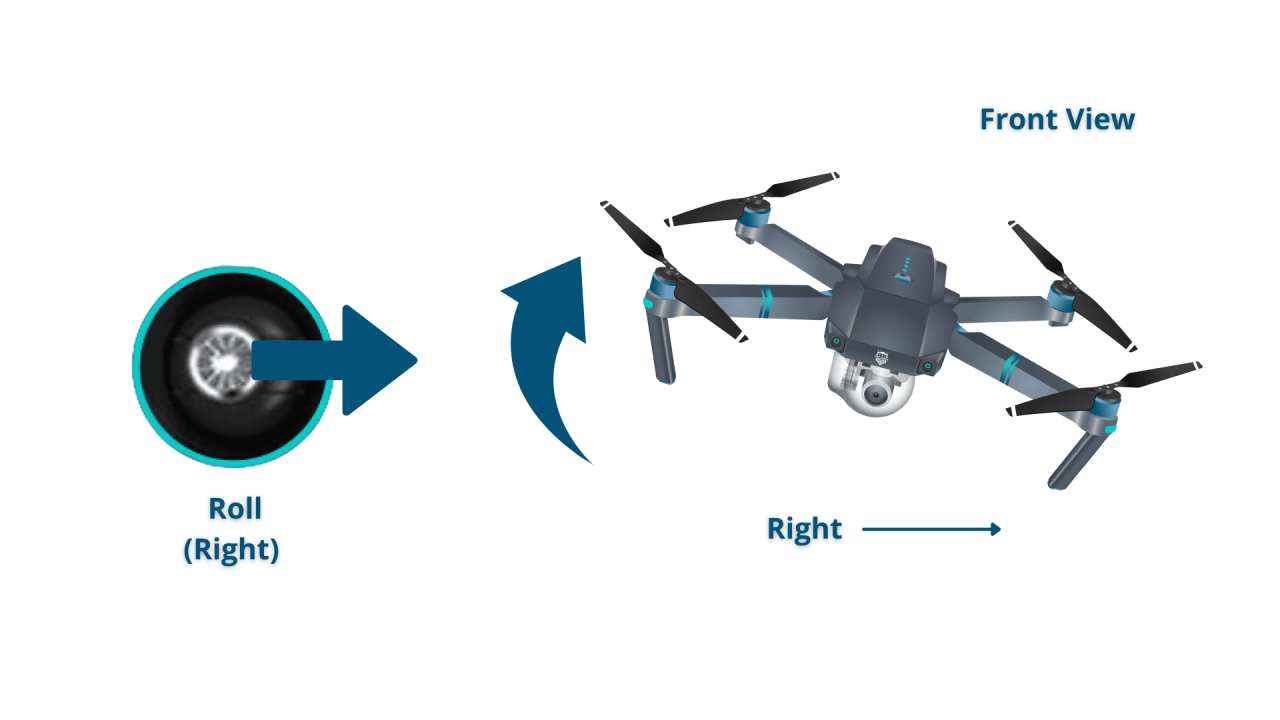
Most drones use four basic controls: throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. These controls manipulate the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space.
Illustrative Description: Imagine a joystick. The vertical axis controls throttle (up/down movement), while the horizontal axis controls yaw (rotation around the vertical axis). Tilting the joystick forward or backward controls pitch (forward/backward movement), and tilting it left or right controls roll (side-to-side movement).
Flight Modes

Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers. GPS mode utilizes GPS signals for precise positioning and autonomous functions like Return-to-Home.
Control Interfaces
Drones can be controlled via various interfaces. Some use joysticks for precise manual control, while others utilize smartphone apps providing intuitive touchscreen controls. Each interface has its advantages and disadvantages; joystick controls offer greater precision, while smartphone apps offer ease of use and access to additional features.
Basic Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is crucial for safe and controlled flight. This involves understanding how to take off, land, hover, and move in different directions using the drone’s controls.
- Taking Off: Gently increase throttle to lift the drone off the ground.
- Landing: Slowly decrease throttle to lower the drone to the ground.
- Hovering: Maintain a constant throttle level to keep the drone stationary in the air.
- Moving in Different Directions: Use a combination of pitch, roll, and yaw controls to move the drone forward, backward, left, right, and diagonally.
Mastering Drone Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques require practice and understanding of the drone’s capabilities. This section will cover GPS stabilization, hovering, ascent/descent, and creating a practice flight plan.
GPS Stabilization
GPS stabilization uses satellite signals to maintain the drone’s position and orientation, resulting in smooth and controlled flight. This is particularly helpful in windy conditions or when performing precise maneuvers.
Stable Hovering
Achieving stable hovering at different altitudes involves precise control of the throttle. Practice maintaining a constant altitude while making minor adjustments to counteract wind gusts or other disturbances.
Smooth Ascent and Descent
Smooth ascents and descents are crucial for safety and stability. Gradually increase or decrease the throttle to avoid jerky movements. Avoid sudden changes in altitude, especially near obstacles.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Practice Flight Plan, How to operate a drone
Beginners should start with simple maneuvers in a safe, open area. Practice taking off, landing, hovering, and moving in different directions. Gradually increase the complexity of maneuvers as your skills improve.
- Takeoff and hover for 30 seconds.
- Move 10 meters forward and hover for 15 seconds.
- Move 10 meters backward and hover for 15 seconds.
- Move 10 meters to the right and hover for 15 seconds.
- Move 10 meters to the left and hover for 15 seconds.
- Ascend 5 meters and hover for 15 seconds.
- Descend to the original altitude and land smoothly.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition, and lighting. This section will cover these aspects and various camera modes.
Tips and Techniques

Use a tripod for steady shots, and consider using ND filters to reduce light and allow for slower shutter speeds in bright conditions. Plan your shots carefully, considering angles and perspectives to capture the best results. Experiment with different flight paths and camera movements.
Lighting and Composition
Lighting is crucial for high-quality aerial imagery. The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) offers soft, warm light ideal for photography. Composition involves arranging elements within the frame to create a visually appealing image. Use the “rule of thirds” to guide your composition.
Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture can significantly impact image quality. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions, but they can introduce noise. Shutter speed affects motion blur, while aperture controls depth of field.
Camera Modes
| Mode | Description | Use Cases | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photo | Captures still images. | Landscapes, buildings, events. | High resolution, sharp details. |
| Video | Records moving images. | Real estate tours, sports events, cinematic shots. | Dynamic visuals, storytelling capabilities. |
| Timelapse | Records a sequence of images over time, creating a sped-up video. | Cloud movements, cityscapes, construction progress. | Compresses time, shows changes over time. |
| Panorama | Stitches multiple images together to create a wide-angle view. | Landscapes, cityscapes. | Wider field of view than single images. |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section will cover common problems, maintenance schedules, and component replacement.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
- Propeller damage: Inspect and replace damaged propellers.
- Battery issues: Ensure proper charging and storage. Replace worn-out batteries.
- GPS signal loss: Ensure clear sky view and sufficient satellites.
- Gimbal malfunction: Calibrate the gimbal and check for physical damage.
- Flight controller problems: Update firmware and check for loose connections.
Maintenance Schedule
Regular cleaning, inspection, and storage are essential. Clean the drone’s body and propellers after each flight. Inspect for damage before each flight. Store the drone in a dry, safe place away from extreme temperatures.
Component Replacement
Replacing components such as propellers and batteries is straightforward. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Ensure you use compatible replacement parts.
Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and other sensors is important for accurate flight. Consult your drone’s manual for specific calibration procedures.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly and legally is paramount. This section covers local and national regulations, permits, restricted airspace, and best practices.
Local and National Regulations
Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your area. These regulations may vary depending on the country, state, or region. Consult your local aviation authority for the most up-to-date information.
Permits and Licenses
In some areas, you may need to obtain permits or licenses to operate a drone, especially for commercial purposes. Check with your local aviation authority to determine if any permits are required.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, proficient operation ensures both successful flights and responsible drone usage.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones
Many areas have restricted airspace, including airports, military bases, and national parks. Flying in these areas is illegal and dangerous. Use drone apps to identify restricted airspace before flying.
Best Practices for Responsible and Legal Drone Operation
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly your drone near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Always follow local and national regulations regarding drone operation.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Register your drone with the appropriate authorities.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that blends technical skill with responsible practice. By diligently following the pre-flight checklist, understanding the nuances of drone controls, and adhering to legal regulations, you can confidently explore the skies and capture breathtaking perspectives. Remember, continuous practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the learning process, and enjoy the incredible world that opens up above.
Clarifying Questions: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes and GPS stabilization are available. Look for models with intuitive controls and safety features.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Charge your batteries after each flight and avoid completely depleting them to extend their lifespan.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this if possible. If not, try to visually locate and recover your drone.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations.
